Data Communication and Computer Networks
Data Communication
The process of sending and receiving data electronically from one location to the other is called Data Communication. Data is transferred using some wired or wireless media.
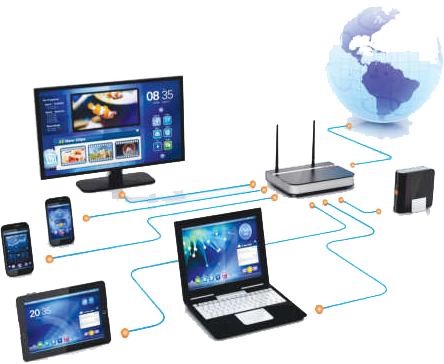
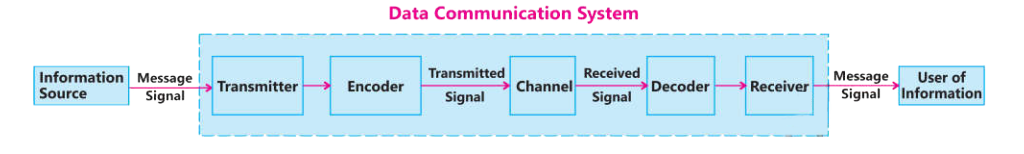
Components of Data Communication:
Following are the main components of data communication system:
- Message
- Sender
- Receiver
- Transmission Media
- Encoders and Decoders
Message:
A message is the data to be sent. It may be text, image, audio, video or combination of these. For example, if you send a picture on WhatsApp to your friend, this picture is a message.
Sender:
A computer or a device that sends a message is called a Sender. It may be a computer, mobile phone, camera, or anything that can send a message over a network.
Receiver:
A computer or a device that receives message is called a Receiver. Again, it may be a computer, mobile phone, fax machine, or anything that can receive the message.
Transmission Media
It is the path on which a message travels from the sender to the receiver. It may be through wired or wireless media.
Encoders and Decoders
Encoders are the devices that convert digital signals into a form that can travel over wired or wireless media on the sender’s side. Decoders receive these converted signals on the receiving side and convert them again into the digital form that can be stored and processed on computers or on other devices.
Communication Media
The path on which data is sent or received over a network is known as Communication Media. There are two main categories of transmission media i.e., wired (physical) and wireless media.
Physical Transmission Media
A physical medium in data communications is the physical path over which a signal transmits. It is also called Guided Media or Bounded Media. Different types of transmission media are used as communication channels. The common types of these physical media are as under:
1. Twisted Pair Cable

A message is the data to be sent. It may be text, image, audio, video or combination of these. For example, if you send a picture on WhatsApp to your friend, this picture is a message.
A twisted pair cable is less expensive as compared to other transmission media. It is a lightweight cable and easy to install.
Advantages of Twisted Pair Cable
- It is relatively easy to implement and terminate.
- It is less expensive.
- Performs best in short distance.
- It is low in weight.
- It is flexible to use.
- It is easy to connect.
- Suitable for data and voice infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cable
- Attenuation (the degradation of signal over distance) is very high.
- It provides poor security and is relatively easy to tap.
- They could break easily because they are thin.
- Low durability (must be maintained regularly).
- Susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
2. Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable consists of a single copper wire surrounded by at least three layers.
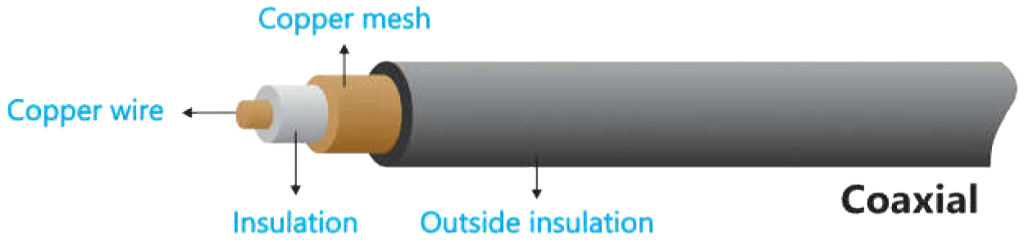
- An insulating material
- A woven or braided meta
- A plastic outer coating
It has a higher data transmission rate as compared to a twisted pair cable. Coaxial cable is frequently used in cable television (CATV) network cabling because it can be cabled over larger distances than twisted-pair cable.
Advantages of Coaxial Cable
- Data can be transmitted at high speed.
- It has enhanced shielding as compared to twisted pair cable.
- It provides advanced bandwidth.
Disadvantages of Coaxial Cable
- It is more expensive compared to a twisted pair cable.
- Any fault in the cable causes the failure of the entire network.
3. Fiber Optic Cable
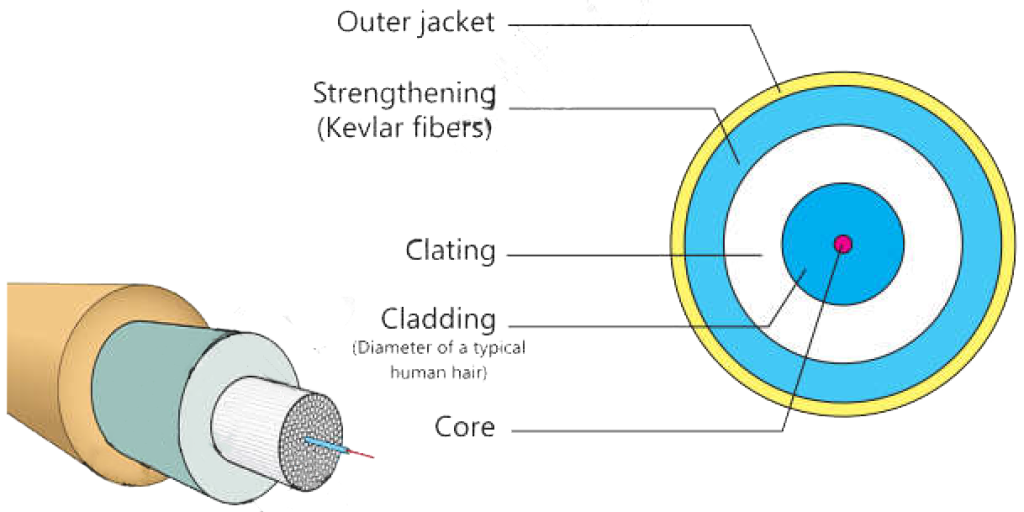
A fiber-optic cable’s core is made up of many small, light-transmitting glass, plastic or silica fibers. The core of fiber optic is the innermost layer. This core is encased in a shield that protects the strands from intrusion. The plastic coating protects the optical fibres from the effects of electromagnetic interference, heat, and cold.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable:
- It provides more bandwidth.
- It carries the data in the form of light. This allows the fiber optic cable to convey the signals at a higher rate.
- It transports the data at longer distances.
- It is more reliable as it is resistant to any temperature changes.
- It is thinner and lighter in weight so it can withstand more pull pressure.
- It is less prone to noise.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Cable:
- Fiber optic cables are costly.
- They require extensive maintenance.
- It is difficult to connect them with other devices.
- They are easily breakable.
- Installation is difficult because of its delicate nature.
Unguided Media
An unguided transmission media transmits electromagnetic waves or signals without using any physical medium. It is also known as wireless transmission. There are three main categories of unguided media as follows:
Radio Waves Transmission
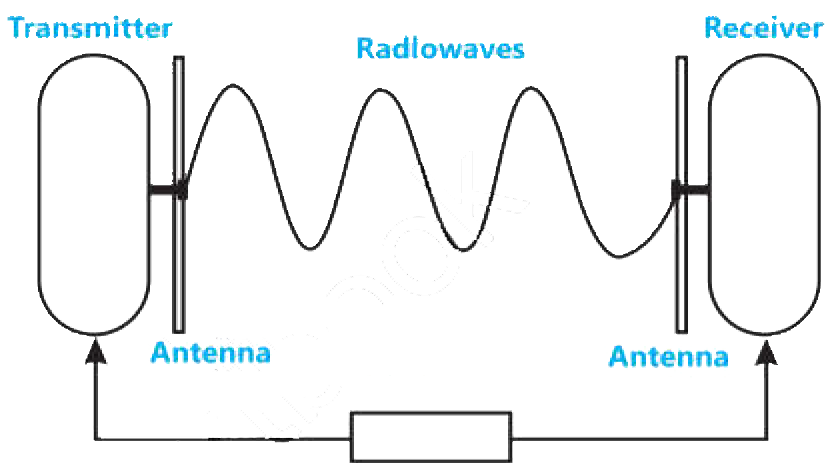
The electromagnetic waves that travel through open space in all directions are known as Radio Waves. These low-frequency electromagnetic waves range from ‘3 kHz to 1GHz’. As radio waves have a low frequency, they can pass through objects like walls, allowing you to receive signals even when you are within a structure.
Examples of radio waves include FM radio, cordless phones, and television.

Do you know?
Hertz is the unit of frequency. It is written as Hz.
Microwaves Transmission
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves that have frequencies between ‘1 and 300 GHz.’ Microwaves only travel in a straight line. The communication between two endpoints and lines of sight becomes much easier to establish once the transmission medium is facing each other.
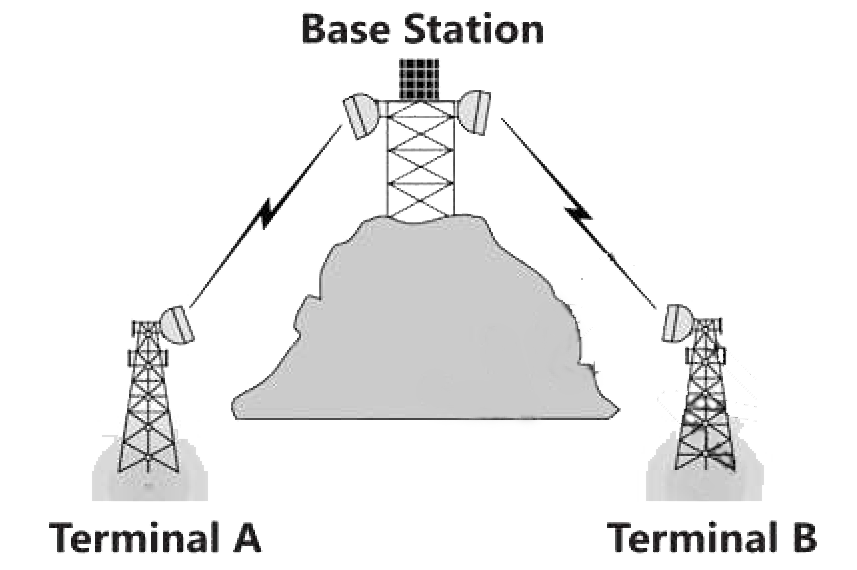
Some examples of the areas where microwaves are used include radio navigation systems, point-to-point communication systems on the surface of the Earth, sensor systems, satellite communications, deep space radio communications, and mobile phone communications.

Do you know?
Number of waves passing through an area per unit time is called frequency.
Infrared Waves Transmission
A wireless method used for communication over short distances is infrared transmission. The infrared spectrum has frequencies between 300 GHz and 400 THz. Due to its high frequency, infrared transmission cannot pass through the walls.
Some examples of the areas where infrared waves are used include TV remote control usage, data transfer between two mobile phones, data transfer between a computer and cell phone, etc.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity)

A Wi-Fi network is simply an internet connection that is shared with multiple devices in a home or business via a wireless router. The router is connected directly to the internet and acts as a hub to broadcast the internet signals to all your Wi-Fi-enabled devices. It provides you the flexibility to stay connected to the internet if you are within your network coverage area.

Li-Fi (Light Fidelity)
Li-Fi is a wireless optical networking technology that uses LEDs for data transmission. In simpler words, Li-Fi is a light-based Wi-Fi that uses light instead of radio waves to transmit information. Li-Fi transmission speeds can go over 100 Gb per second which is 14 times faster than the world’s fastest Wi-Fi.
Wireless Transmission Services
These wireless communication services allow us to send voice, data, movies, photos, and other types of content using air as a medium. It includes:
- Cellular Communication
- Satellite Communication
- Global Positioning System
- Bluetooth
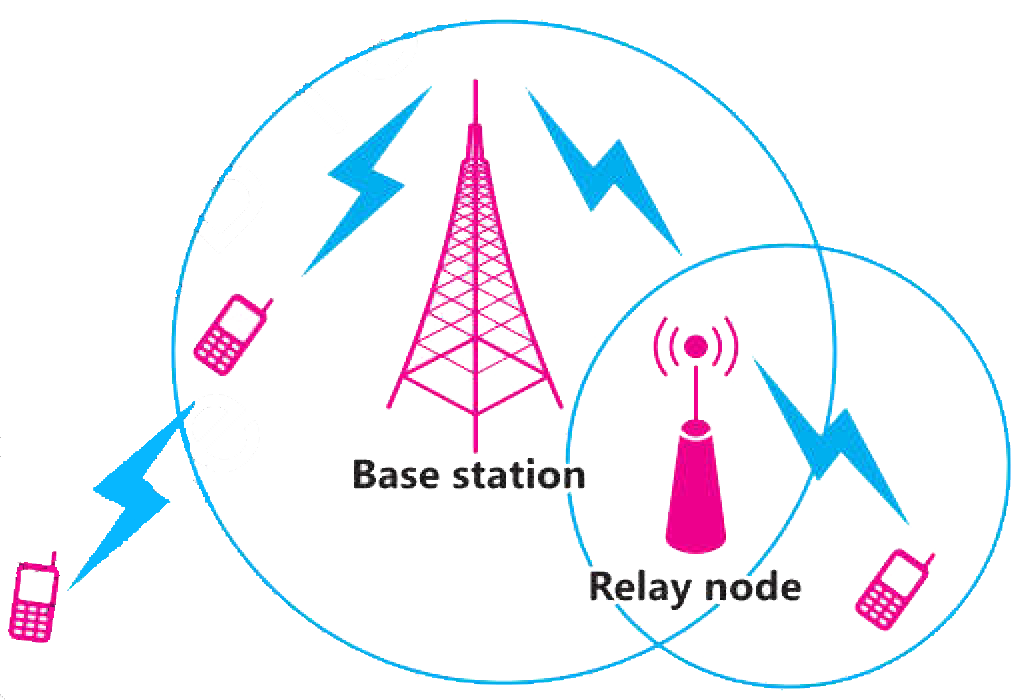
Cellular Communication
A cellular network is a radio network distributed over a vast area through hexagonal cells. Each cell in this network includes a fixed location transceiver known as the base station. These cells together provide coverage of mobile phones over larger geographical areas.

Satellite Communication
Satellite Communication System is an important type of wireless communication. Satellite Communication Networks provide worldwide coverage. Satellite Communication Systems offer different services like telecommunication (by using Satellite Phones), positioning and navigation (by using GPS), broadcasting, internet, etc. Satellite Communication Systems are necessary for mobile, television transmission, and other wireless services.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
GPS is a subcategory of satellite communication. It is primarily used in applications for positioning, navigation, monitoring, and surveying with the help of dedicated GPS receivers and satellites. It is now used in many applications where mobility is needed. GPS receivers are also available in mobile phones.

Do you know?
In 1996, GPS was first made available in automobiles. Its initial applications were used for military purposes.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is another important low-range wireless communication system. It provides data, voice, and audio transmission with a transmission range of 10 meters.
Bluetooth devices are present in almost all smart phones, tablets, and laptops. They are compatible with cameras, audio equipment, wireless Bluetooth receivers, and other devices.
Computer Networks
A computer network is a system that connects two or more devices for sharing and transmitting information. These devices include everything from a mobile phone to a server and may be connected using physical wires or wireless.
Different types of networks are as follows:
Local Area Network (LAN)
In this type of network, two or more computers and devices are connected within a small area, for example, in a room, office building, or a campus. LANs are the best choice for networking in a small geographic area.
Either you have a home network with two or more computers, or you are at your school where more than 20 computers are connected to each other, you are on a LAN.
LAN may use cables or wireless media. WLAN is another name for wireless local area network.
Advantages
- It does not cost a lot of money.
- Data is saved centrally.
- The rate of data transfer is high.
- Central management of resources and software is possible.
- The entire LAN is simple to operate and easy to control.
- The addition of systems to the network is very easy.
Disadvantages
- It covers limited geographic area.
- It is easier for a virus to spread.
- Extremely high maintenance is required.
- The failure of the central device may fail the whole network.
- Extensive cabling may be required.
Devices Used in LAN
In LAN, we use network interface cards, wireless cards, network switches, bridges, and routers etc.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A wide area network spans a large geographic area, such as an entire city, region, or even an entire country or all over the world. WAN connections often involve two or more relatively distant LANs. For example, a WAN may connect an office in Lahore with an office in Faisalabad, it is the geographic distance that makes a network, i.e., a WAN. Internet is the world’s largest WAN.
Advantages
- It covers large geographical area.
- It provides more privacy to its users.
- The communication on WAN is simple.
- Its IT infrastructure is centralized.
Disadvantages
- It has slower speed than LAN.
- Its maintenance is extremely complex.
- The setup cost of WAN is very high.
- It is not a reliable network.
- High-performance devices are needed.
Devices Used in WAN
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) or satellite links are communication devices used for WAN. Long-distance transmission causes greater noise and inaccuracy in WANs than in LANs. Different devices like routers, gateways, manageable switches, modems, and network interface cards are used in WAN.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LAN and WAN
| LAN | WAN |
|---|---|
| 1. LAN is restricted to a small geographical area. It links devices within a building or group of buildings. | 1. WAN covers greater distances and operates worldwide. |
| 2. LAN operates at a faster speed, more than WAN. | 2. WAN is slower than LAN in terms of speed. |
| 3. LAN is privately owned. | 3. WAN ownership might be either public or private. |
| 4. LANs are less expensive than WANs. | 4. WAN is more expensive than LAN. |
| 5. Data transfers more quickly through LAN. | 5. WAN transmits data at a slower rate than LAN. |
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A metropolitan area network connects the local area networks in a city or town. A MAN is a network that is smaller than a typical WAN but larger than a LAN. The best known examples of MAN include Television cable network, Cable Internet, etc.
Advantages
- It offers greater security than a WAN.
- It is larger than LAN and covers the area of a city.
- MAN uses fewer resources than WAN since it is less expensive to implement than WAN.
Disadvantages
- For a MAN connection from one location to another, more cable is needed.
- When compared to LAN, the data rate is slow.
- Making a system secure against hackers is challenging.
- Managing the extensive network is challenging.
- It is more expensive than LAN.
Devices Used in MAN:
Peripheral devices, modems, and wire/cable are utilized to transmit data over MAN. It might involve LANs establishing phone connections and radio waves to link to other LANs.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A virtual private network, or VPN, is a secured connection over the Internet from a device to a network. This secured connection ensures that sensitive data is safely transmitted. It prevents unauthorized people from interfering with traffic and allows the user to conduct work remotely. VPN technology is widely used in corporate environments.
The Internet of Things (IoT)
A network of interconnected computing devices is known as the Internet of Things. These devices include people or things. It is frequently referred to by the acronym IoT.
Any other living thing or artificial product that can be given an IP address and communicate data across a network can be considered an item in the internet of things. Some of its examples include:
- A person with a heart monitor implant.
- A farm animal with a biochip transistor/receiver.
- A vehicle with sensors built in to alert the driver when the tyre pressure is low.

Do you know?
By 2027, there are expected to be 41 billion IoT devices.
Examples of Internet of Things (IoT)
- Connected appliances
- Smart home security systems
- Autonomous farming equipment
- Wearable health monitors
- Smart factory equipment
- Wireless inventory trackers
- Biometric cyber security scanners
Embedded Computers
A dedicated computer system that is an essential component of a bigger machine or system is known as an Embedded Computer or Embedded PC. An embedded computer typically has a specific purpose only. These computer systems are commonly used in industries, vehicles, traffic control systems, etc.
Embedded Systems
An embedded system is a microprocessor-based computer hardware system with software that is used to perform a specific function, either as a separate system or as a part of a large system. Examples of embedded systems include digital cameras, smart watches, MP3 players, appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens, etc.
Edge Computing
The word edge in computing means geographic distribution. Edge computing is a computing model in which we focus on bringing computing devices and sources of data as closely as possible to improve response times and save bandwidth. Edge computing refers to architecture rather than a specific technology. In this way, we can minimise the number of long distance communication costs.
Following are some applications of Edge Computing:
- autonomous vehicles
- remote monitoring of assets in the oil and gas industry
- predictive maintenance
- in-hospital patient monitoring
- cloud gaming
- traffic management
Data Analytics
Data analytics is the science of analysing raw data to make assumptions about that information. Many of the techniques and processes of data analytics have been devised or used as automated procedures and algorithms that work over raw data for human consumption.
Data analytics:
- help a business optimise its performance.
- help individuals and organizations to organize data
- typy examine raw data for insights and trends.
Glossary
| Convey | transport or carry to place |
| Delicate | easily broken or damaged |
| Susceptible | Likely to be influenced by something |
| Bandwidth | maximum amount of data transmitted in a given amount of time. |
| Hexagonal | having six sides and six angles |
| withstand | remain undamaged or unaffected |
LET’S HAVE A LOOK
- A physical medium in data communications is the physical path over which a signal transmits. It is also called Guided Media or Bounded Media.
- Twisted pair cable is made by twisting two separate insulated wires together that run parallel to one another.
- The electromagnetic waves that travel through open space in all directions are known as Radio Waves.
- Coaxial cable is frequently used in cable television (CATV) network cabling because it can be cabled over larger distances than twisted-pair cable.
- The plastic coating protects the optical fibres from the effects of electromagnetic interference, heat, and cold.
- An unguided transmission transmits electromagnetic waves without using any physical medium. Therefore, it is also known as wireless transmission.
- A cellular network is a radio network distributed over a vast area through hexagonal cells.
- GPS is a subcategory of satellite communication.
Exercise
- Multiple Choice Questions: Tick the correct answer.
- Write ‘T’ for True and ‘F’ for False in the boxes
- Answer the following short questions:
- What is meant by the augmented reality?
- What are some of the applications of AI?
- What is holographic imaging?
- What are the primary difficulties in robotics?
- What are the other names used for self-driving cars?
- State the applications of 3D imaging.
- Which device is used to experience virtual reality?
- What is the main purpose of using Computer Assisted translation?
- How can you create a hologram at home?
- What makes 5G better than previous ones?
- Answer the following long questions:
- Write a note on blockchain.
- 2. What are the differences between Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality?
Learning Activities
Activity 1: (Research and Present)
- Divide the students into two groups.
- Name both groups as Group A and B respectively.
- Ask each group to research about various emerging technologies of their choice and present features, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
Activity 2: (Mapping)
- Divide the students into suitable pairs.
- Ask each pair to open Google Maps on their computer/smartphone.
- Ask them to type their home address in the search bar and click Search.
- Ask them to click Get Directions and type the school’s address in the starting directions bar and click Search.
- Ask them to look at the map (or satellite view) and check if that’s the route of you getting to school.





You must be logged in to post a comment.